- Floppy Disk Drive
- Hard Disk Drive
- CD/CDRW
- DVD/DVDRW
- Flash ROM
1. Floppy Disk Drive (FDD) :- A Floppy Disk Drive is a disk drive that enables a user to save data to removable disk. Initially, FDDs used the 5 1/4" floppy disks, which were later replaced with 3 1/2" disks. However, with the advent of removable hard disks, and flash drives, many computers no longer use floppy disk drives.
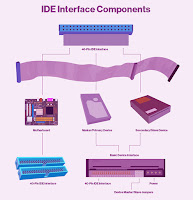
The Pentium motherboard provides a standard 34-pin connector for interfacing with FDD. A 34-pin flat ribbon cable is used to connect the motherboard to FDD. This cable connects the motherboard's FDD interface with one or two floppy disk drives. Floppy Disk Controller (FDC) uses I/O address range 370 to 37Fh. FDD divides the floppy disk into 80 tracks per side, with 9 or 18 512-byte sectors per side. This provides the system with 720KB ( 737,280 bytes) or 1.44MB (1,474,560 bytes) of storage. For power supply, FDD uses a Berg connector as illustrated in the figure below. The FDD controller is assigned the IRQ-6 in PC-compatible systems. The FDD controller generates an interrupt signal each time it receives a Read, Write, or Format command from the system.
Floppy Drive Interface Cable:- The FDD interface cable is used to connect the FDD to the motherboard. The FDD cable in the figure shows traditional five connectors configuration. It has connectors for 5.25" drives, as well as 3.5" drives, and 34-pin wide. However, 5.25" drives are rarely used now-a-days. "Cable Twist" in the floppy cable is located between the two pairs of connectors intended "A" and "B" floppy drives. This twist causes the drive at the end of the cable to appear as A: to the system and the one in the middle to be as B:.